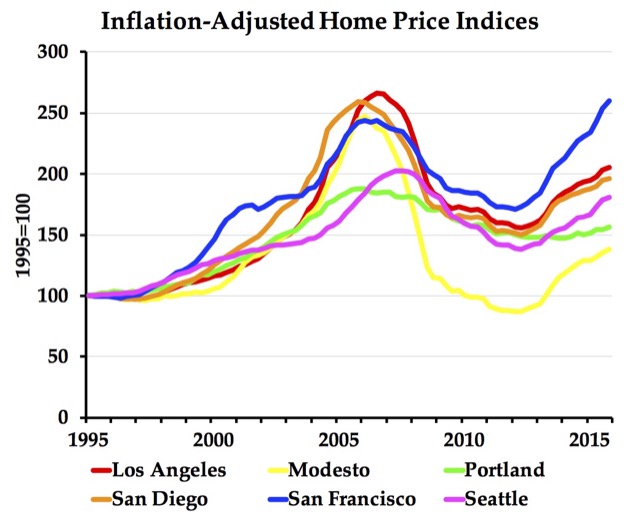
A new report from Hawaii’s Grassroot Institute argues that Hawaii’s land-use laws must be repealed because they discriminate against low-income minorities. Hawaii was the first state to pass a land-use law in 1961, and not coincidentally it has the least affordable housing in the nation.
The 2014 American Community Survey found that median home prices in Hawaii were 6.7 times median family incomes, compared with the national average of 2.7. These high prices had pushed low-income minorities to leave the state: while urban Honolulu had grown by 12 percent between 2000 and 2010, the urban area’s black population declined by 4 percent.
Hawaii’s 1961 land-use law divided lands in the state into urban, agriculture, and conservation (later a fourth category, rural, was added). While the supposed purpose was to protect Hawaii’s agricultural sector, in fact it destroyed it because high housing prices increased labor costs and plantations and canneries can’t compete with those in places like Fiji and Costa Rica.