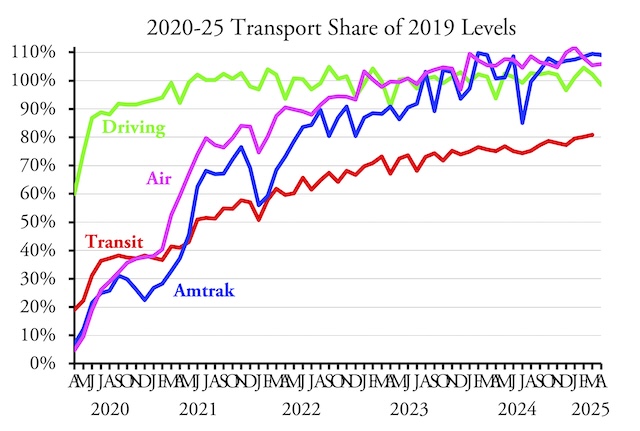
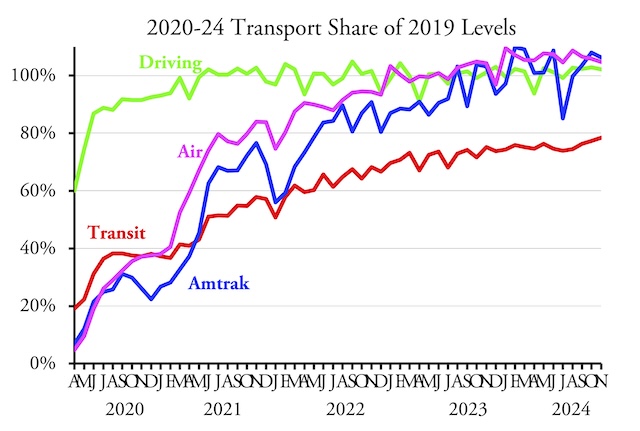
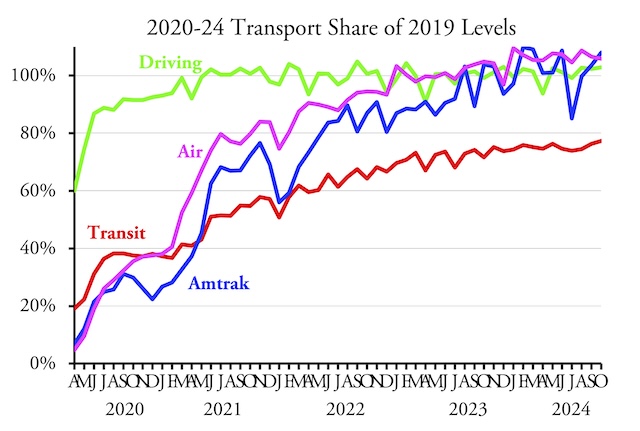
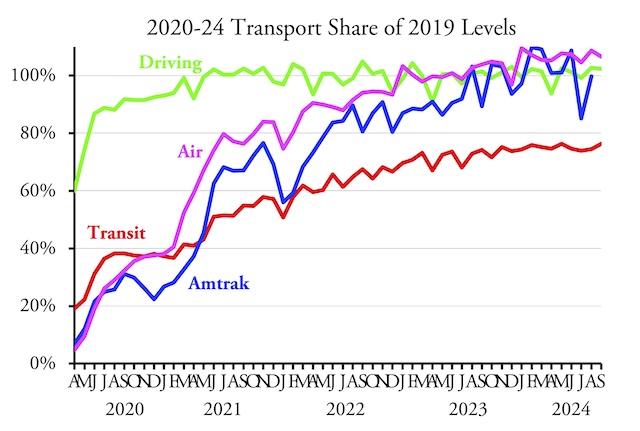
Amtrak carried 9.0 percent more passenger-miles in April 2025 than in the same month before the pandemic, according to the state-owned company’s monthly performance report. The airlines did almost as well, carrying 5.8 percent more riders in April than in 2019. However, Americans drove only 98.5 percent as many vehicle miles in April as in 2019.
April transit data are not yet available and will be posted here as soon as possible after the FTA releases them.
It’s hard to guess why driving dropped, at least as a percentage of 2019. The economy was slowing, rail freight was declining (though still more than 2019), but perhaps truck freight had fallen. Continue reading