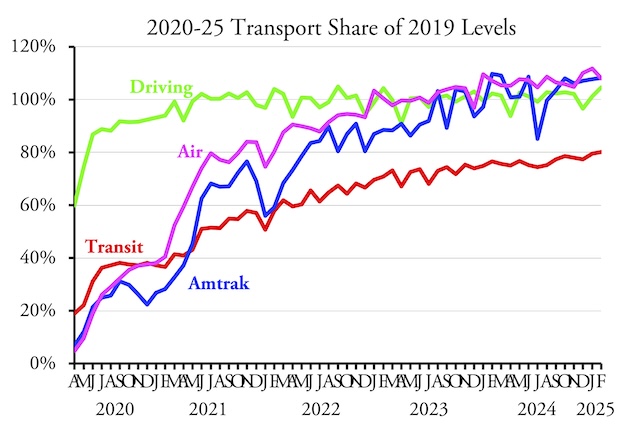
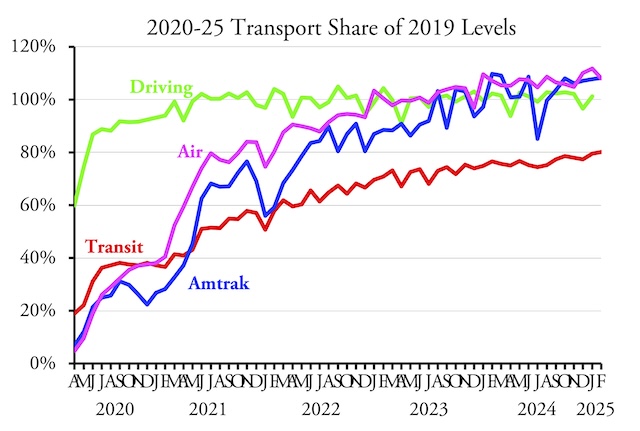
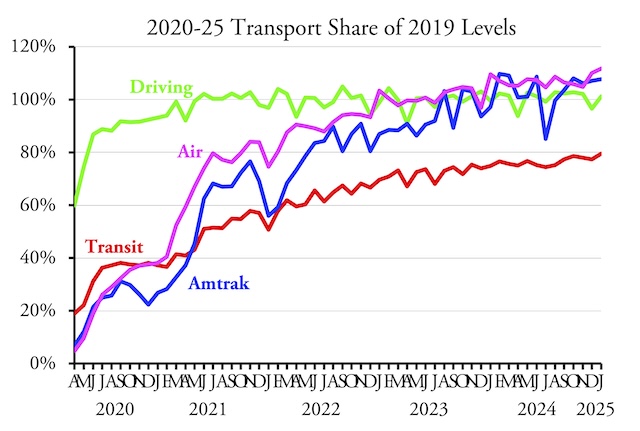
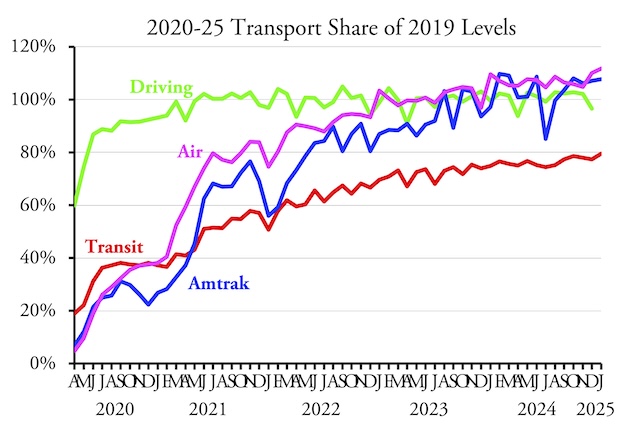
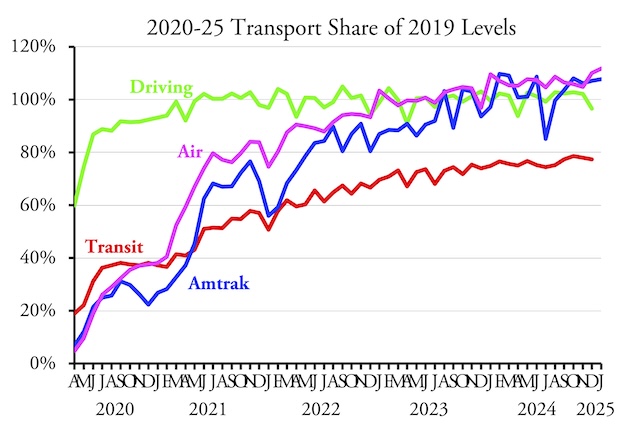
Americans drove 4.6 percent more miles in February 2025 than in the same month of 2019, according to data released yesterday by the Federal Highway Administration. Both urban and rural driving surpassed 2019 levels, as well as driving on all major types of roads: interstates, other arterials, and other roads. This is the first time since the pandemic that driving on all types of roads exceeded 2019 levels.
The February release presented some surprises. While February driving in Massachusetts was still less than 90 percent of pre-pandemic miles, Californians drove 5.5 percent more, Hawaiians 8.0 percent more, and Oregonians 7.0 percent more miles than in 2019. The only western states where driving fell short of 2019 miles were New Mexico, Washington, and Wyoming. Continue reading