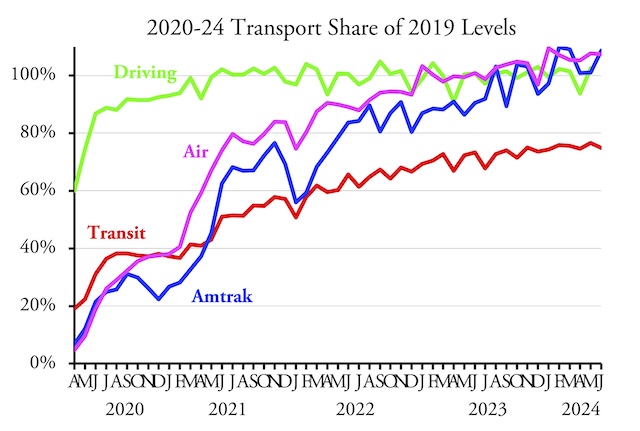
Amtrak carried 654 million passenger-miles in June of 2024, an 8.6 percent increase over the same month in 2019, according to the state-owned company’s monthly performance report issued last Friday. Amtrak passenger-miles have been ahead of pre-pandemic numbers for every month since February 2024.
See last week’s post for transit results. Data are not yet available for driving but will be posted here as soon as they are.
Last week, I noted that the Transportation Security Administration counted 7.4 percent more airline passengers in June of 2024 than 2019. This number is not strictly comparable to the Amtrak number as this is passengers while the Amtrak number is in passenger-miles. The Bureau of Transportation Statistics keeps track of airline passenger-miles but releases the data nearly two months after Amtrak. Continue reading