One of the more interesting presentations at the 2017 American Dream conference was by Alain Bertaud, a French demographer currently working at New York University. He has compared urban areas all over the world to see how transportation has influenced the layout of those areas.
Click any image for a larger view.
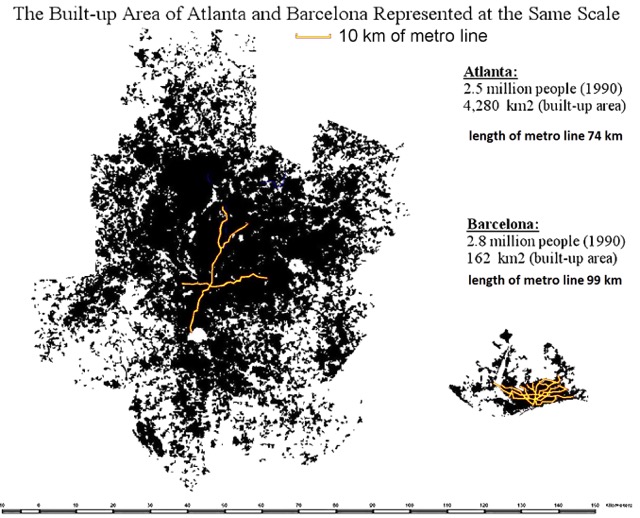
He started by comparing Atlanta with Barcelona, Spain. Although both have about the same number of people, Barcelona occupies about 63 square miles while Atlanta covers 1,650 square miles. Barcelona has about 62 miles of rail lines, while Atlanta had about 46 when Bertaud was making his comparison (it’s up to 52 today). In order for Atlanta’s rail system to provide the same level of service to its residents as Barcelona’s, the region would need to build another 2,350 miles of rail lines. At current construction prices, that would cost at least $700 billion. Continue reading