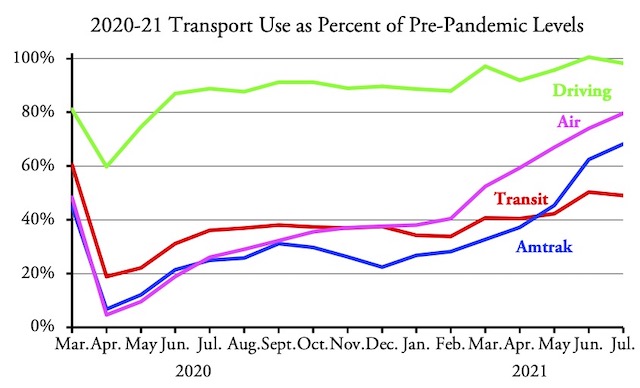
China’s high-speed system is caught a debt trap, having to borrow money to repay the loans taken out to pay for rail construction. Although a few lines claim to be profitable, most are not. As a result, says an article published by New Delhi think tank Observer Research Foundation, since 2015 interest payments on China State Railway debt has been greater than high-speed rail revenues.
The article (all but the last four paragraphs of which is used as the narrative for the above video) was written as a warning that “Poorer countries trying to emulate HSR must be mindful of the pitfalls.” But it is equally valid as a warning to richer countries, where construction costs are higher and where the value of passenger rail is lower due to extensive networks of intercity highways and airports. Continue reading