The American Petroleum Institute has a web page showing how much of the price you pay for gasoline goes to the government in each state. They include ordinary gas taxes as well as sales taxes on gasoline, but not taxes paid by the oil companies themselves.
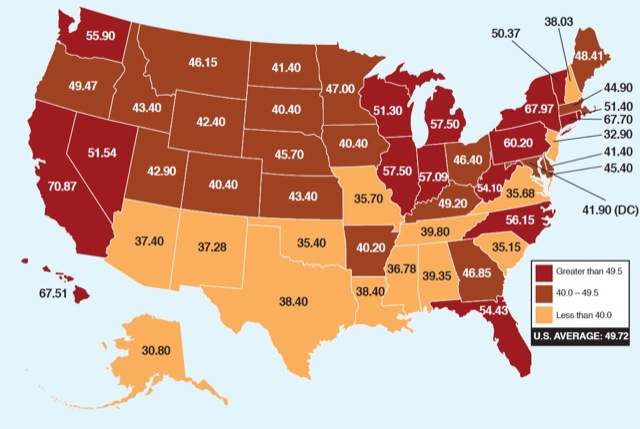
Click image to go to the API web site for more detail.
Their goal, I suppose, is to show that the oil companies aren’t making anywhere near as much profit off of gasoline as the government is. But the map also shows some clear geographic differences. First, the lowest taxes are in the sunbelt, while the highest are in ultra-blue states on the coasts and upper Midwest. Second, the range in gas (excise) taxes is quite wide, from 10.5 cents per gallon in New Jersey to 37.5 cents in Washington state.










