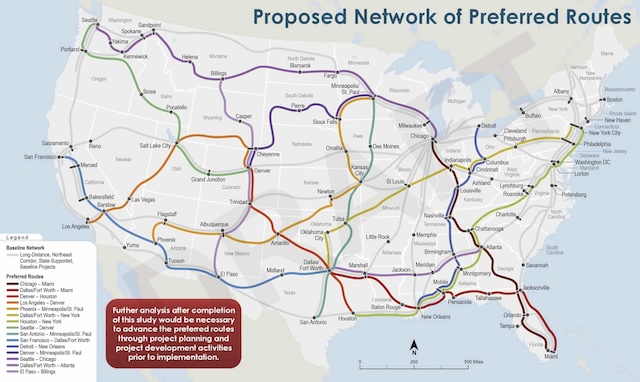
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) estimates that adding 15 new overnight routes to Amtrak’s system will cost taxpayers $46 billion to $59 billion (see pages 80 to 159 of this 18.8-MB file) plus increase Amtrak’s annual operating costs by $1.1 billion to $1.6 billion. The FRA did not estimate ridership or fare revenues, but it did estimate that adding these routes would reduce driving by 0.014 percent and the annual number of highway accidents by 0.016 percent.
Click image for a larger view.
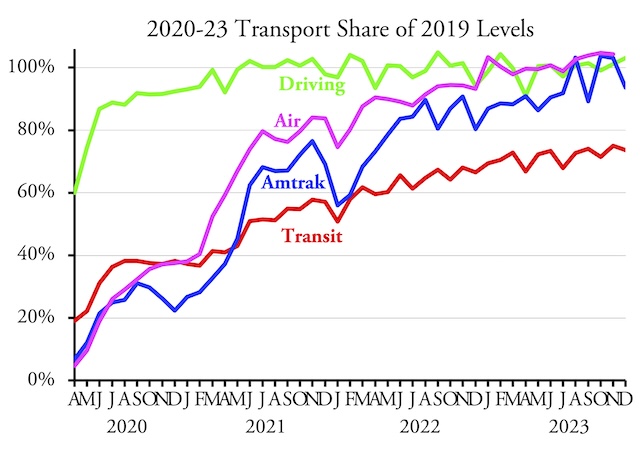
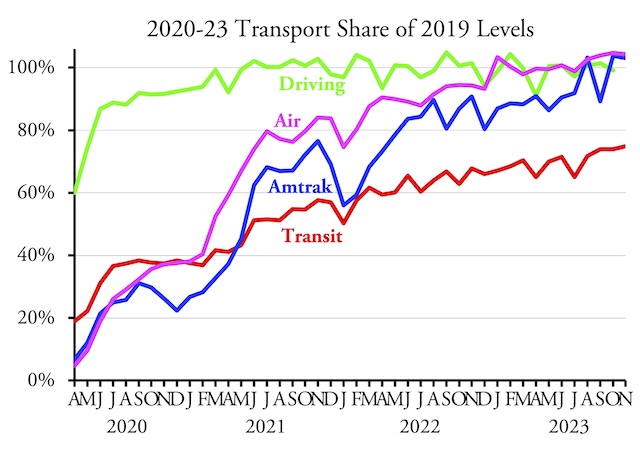
Amtrak currently has 15 overnight train routes that carried just over 2.0 billion passenger-miles in 2023 (see page 7). These routes cost $1.3 billion to operate in that year (not counting depreciation) and earned just under $600 million in fare revenues. Amtrak admits all of them except the Virginia-Florida Auto Train lost money, and when depreciation is counted that train probably lost money as well. Continue reading
 The official portrait of Mayor Goldschmidt.
The official portrait of Mayor Goldschmidt.