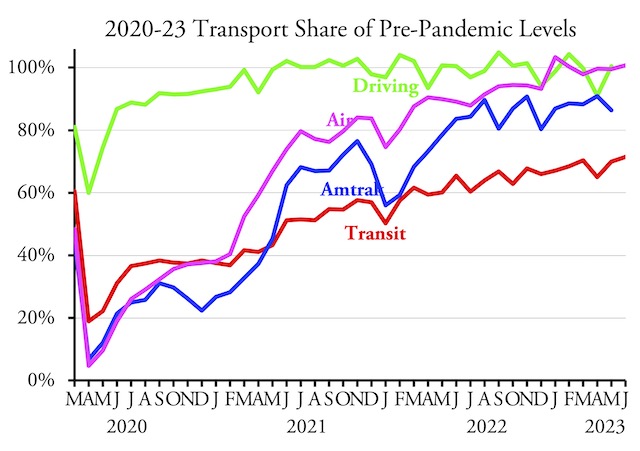
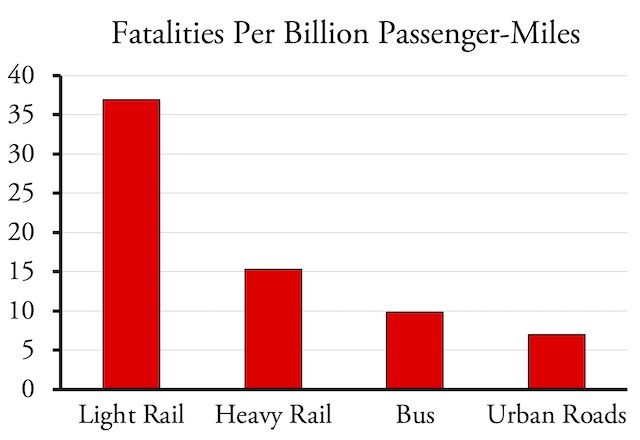
Land-use and transportation planning is supposed to follow a rational planning process. That process includes defining the problem that needs to be solved, identifying alternative solutions, evaluating the alternatives, developing a final plan based on the best alternative or combination of alternatives, implementing the plan, monitoring the effects to see how well reality matches planning assumptions, and using the results of that monitoring as feedback into future plans.
 This 1969 book describes the rational planning process on page 95.
This 1969 book describes the rational planning process on page 95.
The rational planning model has been around since at least 1969. Yet today, more than 50 years later, hardly any government agency follows this model. Instead, most government plans I’ve reviewed follow what can only be called an irrational planning process. Continue reading