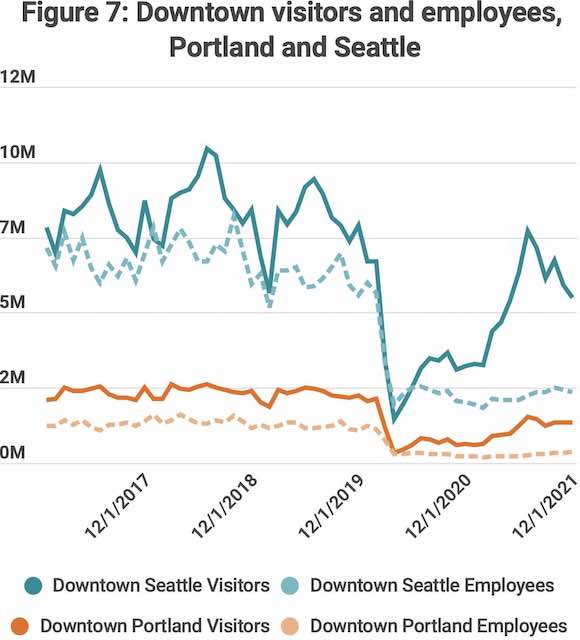
The number of people working in downtown Portland dropped from more than 103,000 in mid-2019 to 13,000 in mid-2020, according to a State of the Economy report recently published by the Portland Business Alliance. The report doesn’t actually show numbers, but the chart below, which I took from the report, can be used to make pretty close estimates.
This chart is taken from page 3 of Portland Business Alliance’s State of the Economy report. Click image for a larger view.
By the end of 2021, the downtown area had recovered to about 34,000 workers, still less than a third of pre-pandemic numbers. The pandemic may not be the only factor depressing downtown employment: Black Lives Matter protests that began in May 2020 resulted in “numerous instances of arson, looting, vandalism, and injuries,” many of which affected downtown businesses and will probably continue to do so well into the future. Continue reading