Media reports say that a study from Carnigie Mellon has found that micromobility — a fancy word for electric bikes — can relieve traffic congestion and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, this is largely based on wishful thinking.
Electric bicycles in California. Photo by waltarrrrr.
The study looked at 2014 travel data for Seattle and concluded that “18% of short trips in Seattle can be replaced by micromobility modes” based on the age of the people making the trip and their trip purpose. “If even 10 percent of short car trips during peak afternoon travel were replaced with micromobility,” reports say, it would reduce congestion and greenhouse gas emissions by 2.76 percent. Continue reading



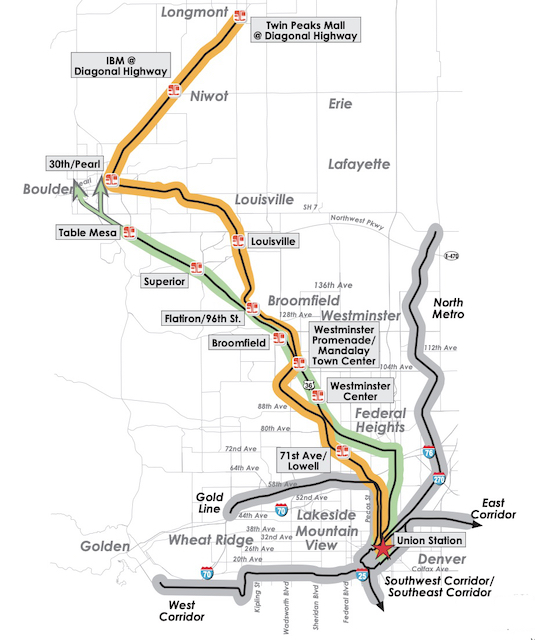 The green line is the existing bus-rapid transit line while the circuitous orange line is the proposed rail route to Longmont. The thick grey lines are other rail transit routes that are nearly all in service today. If Longmont were really a worthwhile destination, the logical thing for RTD to do is extend the bus-rapid transit line to Longmont. But Longmont officials were promised a train and they demand to have a train.
The green line is the existing bus-rapid transit line while the circuitous orange line is the proposed rail route to Longmont. The thick grey lines are other rail transit routes that are nearly all in service today. If Longmont were really a worthwhile destination, the logical thing for RTD to do is extend the bus-rapid transit line to Longmont. But Longmont officials were promised a train and they demand to have a train.