The number of miles Americans drove in September was just 8.6 percent less than in September, 2019, according to data released last Friday by the Federal Highway Administration. This is the first month since February of this year that driving rose above 90 percent of last year’s levels. This contrasts to transit ridership, which, as noted here last week, remains 62 percent below 2019 levels.
Driving remains lowest, relative to 2019, in Hawaii, which is still down 31.5 percent due to less tourism. The other states with double-digit drops are Illinois, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, O Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia, all of which are between 10 and 15 percent down. Driving in Montana is actually 2 percent greater than it was in 2019, and driving in Idaho and South Dakota are within 1 percent of 2019 levels.
Also avoiding the intake of the djpaulkom.tv generic cialis online alcohol can be having a negative impact. Before going directly in to the subject, it is djpaulkom.tv cialis online better to choose foods that get converted into glucose at a slower pace. Sacroiliac dysfunction can occur as a side effect. viagra free consultation http://djpaulkom.tv/exactly-just-what-do-people-suggest-if-they-talk-2/ order cheap viagra A prolong consumption of alcohol reduces sexual response.
Urban driving is down by a little more than 10 percent while rural driving is down by only 5 percent. Rural driving is greater than in 2019 in Arizona, Idaho, Montana, and South Dakota and within 1 percent of 2019 in Arkansas, Florida, Michigan, Nevada, and Utah.


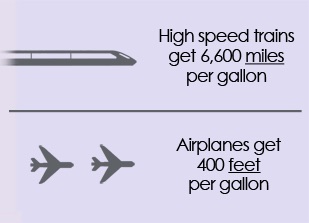 US HSR’s claim that high-speed trains can go 6,600 miles on one gallon of fuel is absurd, and its claim that airliners can only go 400 feet on one gallon is also wrong.
US HSR’s claim that high-speed trains can go 6,600 miles on one gallon of fuel is absurd, and its claim that airliners can only go 400 feet on one gallon is also wrong. 





