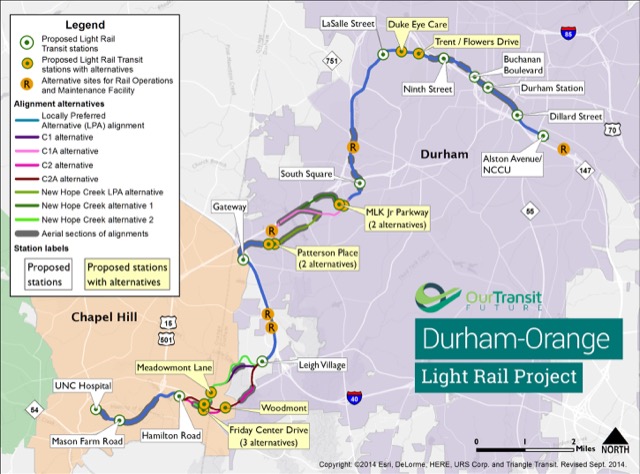
After holding a final public hearing last night, officials in Durham, North Carolina will probably decide next week to build a $3.3 billion ($2.4 billion construction plus $900 million interest on debt) light-rail line from Durham to Chapel Hill. It is hard to imagine any place that is more poorly suited for rail transit.
The region’s population density is less than 2,000 people per square mile. Except for the universities, there are no real concentrations of jobs. The biggest job center in the region, Research Triangle Park, has about 50,000 jobs spread out over 11 square miles, but it isn’t even on the proposed light-rail line. To make matters worse, the proposed 17.7-mile rail route is so circuitous that someone on a fat-tire bicycle could probably beat the train by taking a shorter route.