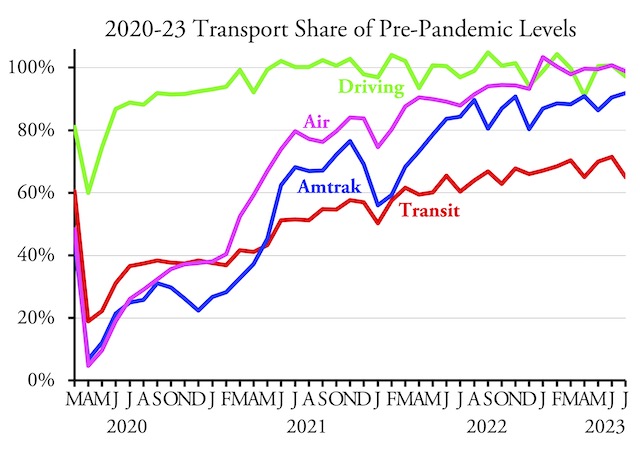
“Flush with cash” from the 2021 infrastructure bill, says the Wall Street Journal, Amtrak hopes to “double ridership by 2040.” That’s an ambitious goal, and yet one that is totally insignificant.
Amtrak’s logo looks like a pointless arrow, but the real point is to spend lots of money.
Amtrak carried 5.1 billion passenger-miles in 2022. Divide that among the 332 million Americans and Amtrak carried the average American 15 miles. That compares with 16,000 miles of per capita travel by automobile and more than 2,100 miles by domestic airline. The Census Bureau expects the nation’s population to rise to 373 million by 2040, so even if Amtrak could double ridership, which is unlikely, per-capita intercity rail travel would grow to only about 27 miles per year. In other words, Amtrak will still be irrelevant to most Americans. Continue reading