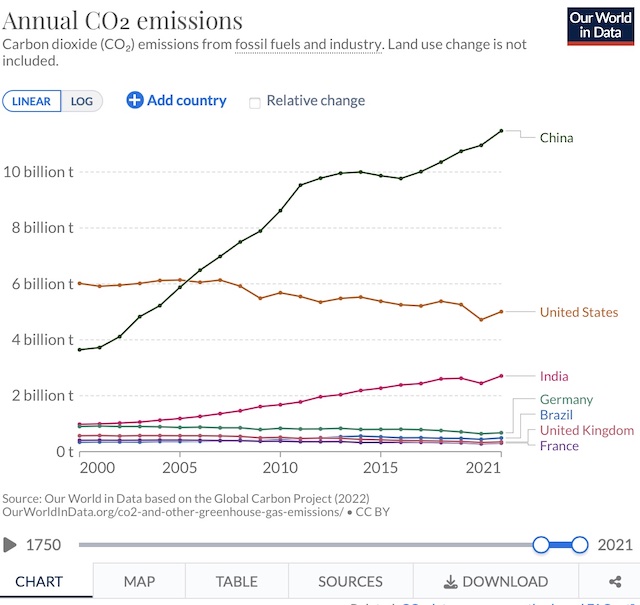
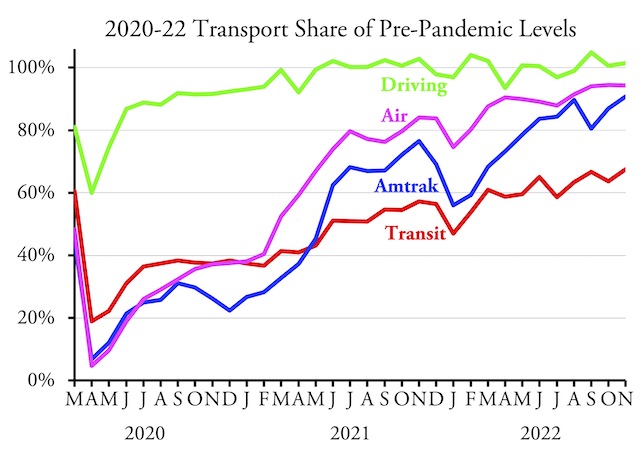
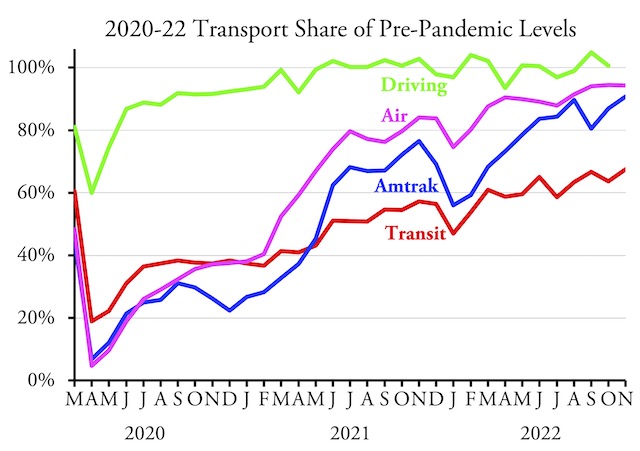
We can’t replace petroleum-fueled motor vehicles with ones powered by electricity, according to a new report, because mining enough lithium to power the batteries for those electric vehicles will destroy the world. Or part of it, anyway. The only solution, says the report, is for countries like the United States to replace private vehicles with public transit.
The only way to prevent this, according to a group called the Climate and Community Project, is to ban cars.
Why is it that, no matter what the problem, leftists think the only solution is to ban cars and spend more money on mass transit? According to a sociologist I once knew named John Finley Scott — who is better known for having created one of the first mountain bikes than his sociological research — most auto opponents are people who didn’t learn to drive until their late 20s or later, by which time they knew they were mortal and found driving to be terrifying. They can’t imagine anyone actually liking cars or driving, so they see nothing wrong with ridding the earth of such an evil invention. Continue reading