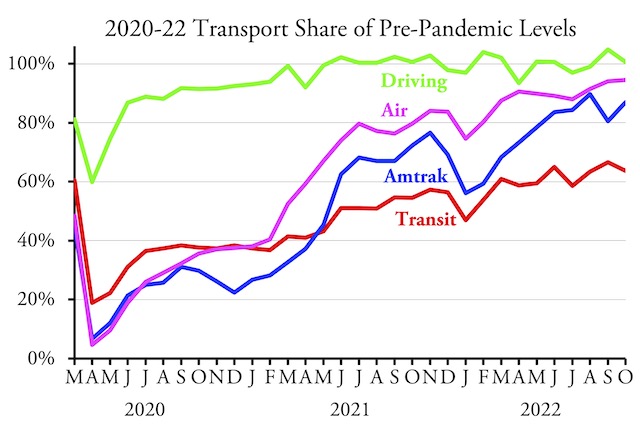
Despite record fuel prices, Americans drove almost 1 percent more miles in June 2022 than they did in June 2019, according to data released on Saturday by the Federal Highway Administration. Driving declined on urban interstate freeways, but it increased on other urban roads as well as all types of rural roads.
See the previous post for sources of Amtrak data and the post before that for sources of data for transit and air travel.
The nationwide average price of regular gasoline climbed from $4.58 a gallon on June 1 to a record $5.02 on June 14. Supposed experts claimed that prices would “stay high for a long time,” but instead they have fallen every day since the 14th, reaching $4.80 at the end of June and $3.90 as of yesterday.
On a miles-per-day basis, Americans drove 1.1 more miles in June than in May and 5.1 percent more in June than in April, when gas prices were 60 to 80 cents a gallon less than in June. This suggests that people are less deterred by high fuel prices than auto opponents would hope.
As noted a few days ago, transit ridership made a leap in June, with average daily ridership being 4.5 percent greater than in May. But since Americans travel almost 100 times as many passenger-miles per year by automobile as by urban transit, a large increase in transit ridership translates to a small decline in driving. That increase in transit ridership may have compensated for the decline in urban interstate driving, but lower fuel prices in July and August will probably lead to an increase in urban driving and a compensatory drop in transit travel.
When compared with June 2019, driving grew the most in Indiana (18%), Florida (16.5%), Connecticut (12.9%), Georgia (11.6%), Louisiana and Texas (each 11.7%). It fell the most short of 2019 miles in the District of Columbia (-19.2%), Delaware (-16.1%), Montana (-11.5%), Oregon (-8.7%), and Washington (-8.5%).