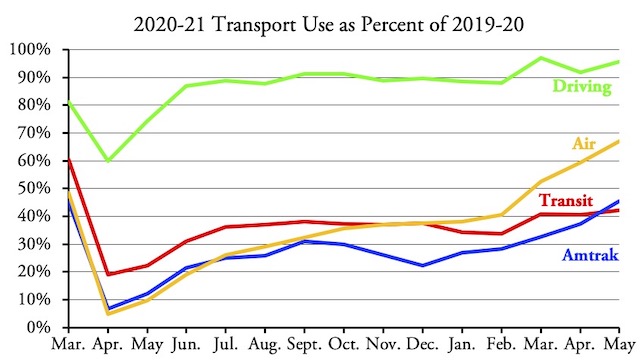
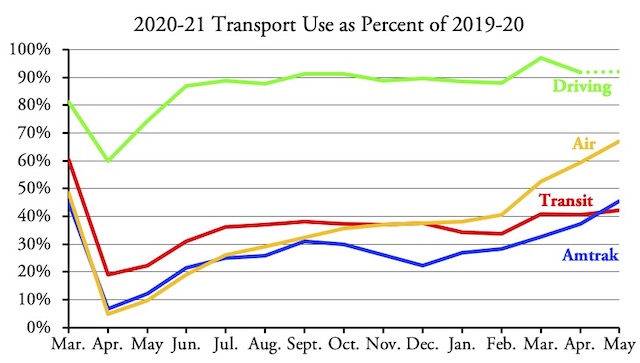
Before the pandemic, two people commuted from Podunk, Michigan to Detroit, a drive of about one hour. If someone built them a high-speed rail line, they could save nearly half an hour, assuming they don’t decide to work at home. Of course, the fares they pay would never come close to covering the $6 billion cost of building the rail line, but who cares about the cost per rider?
“Who cares?” seems to be the attitude of the Northeast Corridor Commission, which consists of Amtrak and the commuter rail agencies that run trains on part of the Boston-to-Washington rail system. Where its 2010 master plan called for spending $52 billion in the corridor, the 2021 plan demands $117 billion to keep running trains in the corridor. But who cares about the increased cost? Continue reading