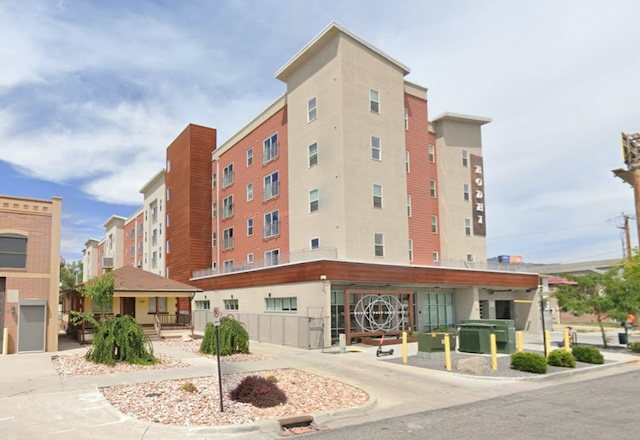
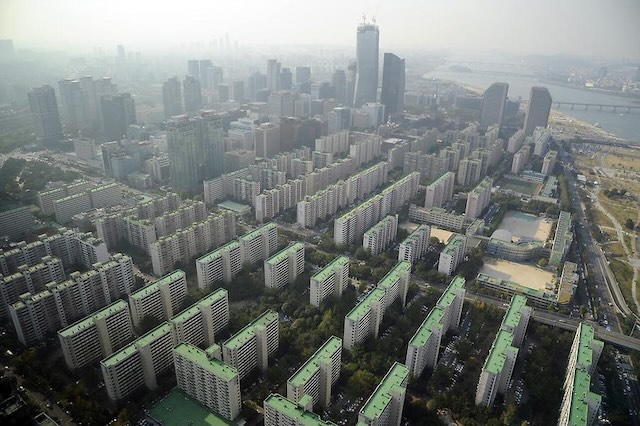
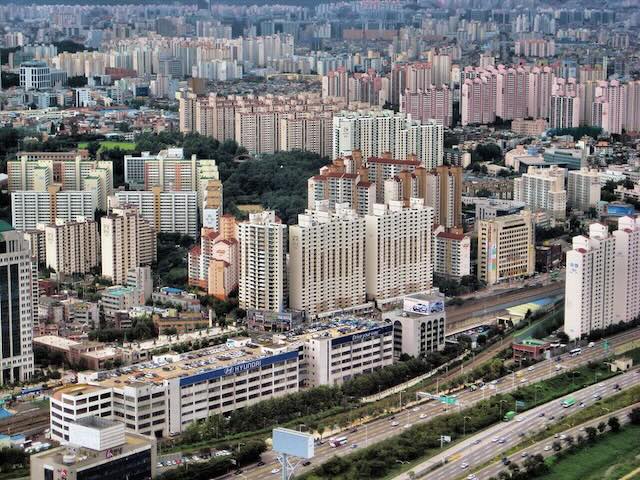
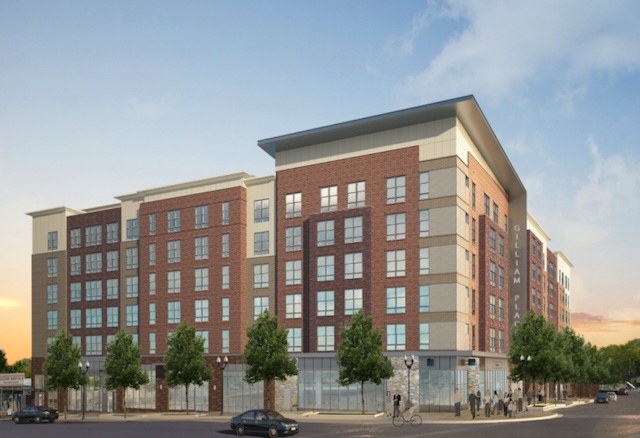
In December, I pointed out that Silicon Valley’s transit system was designed for the 1910s and suggested a way to redesign it so that it would serve a 2020s urban area. Last month, the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA) announced that is attempting the exact opposite strategy: it wants to turn Silicon Valley into a 1910s urban area.
Planned high-density developments aim to turn San Jose into a Greenwich Village lookalike. Source: Republic Urban Properties.
Last week, a Silicon Valley group called Opportunity Now published my assessment of why this strategy is bound to fail. Instead, it will waste a lot of tax dollars and enrich a few property developers without making the region’s housing more affordable or helping regional mobility.