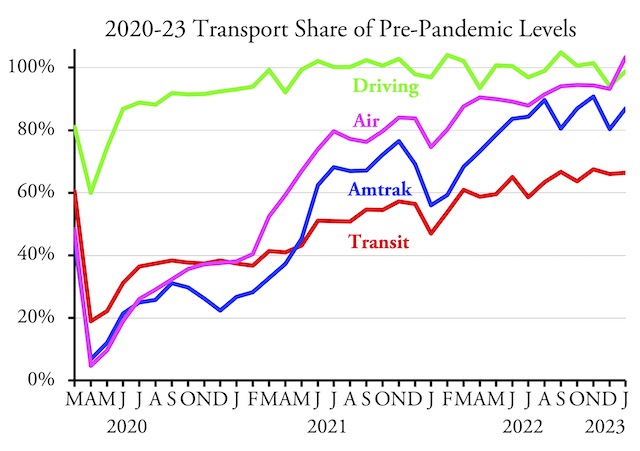
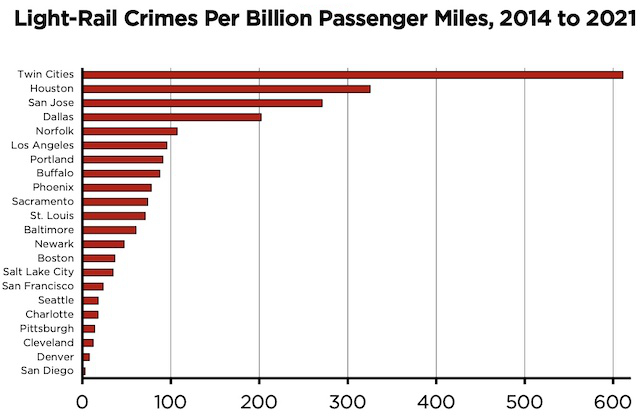
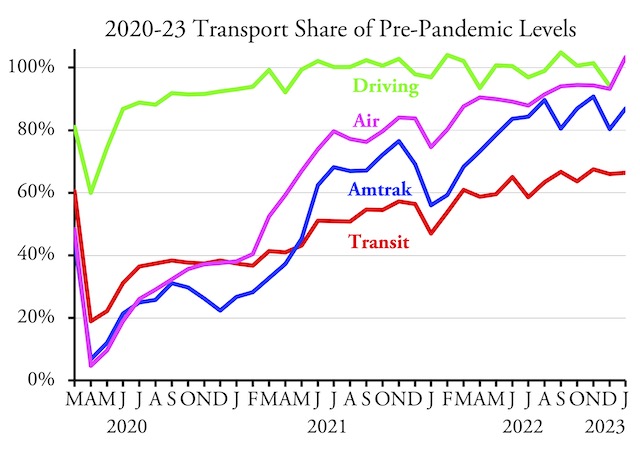
New York’s Metropolitan Transportation Authority will soon go off a fiscal cliff, partly due to reduced ridership but also due to bad management. But never fear: New York legislators have a solution. They propose to tax Netflix and Uber to raise money to keep the subways and buses running.
One of the most expensive transit projects in the world, the Second Avenue Subway is expensive partly because the MTA spent more on consultants than it did on actual construction. MTA Capital Construction photo by Rehema Trimiew.
Taxing Uber makes kind of a warped sense, like taxing jet airliners in order to subsidize Conestoga wagons. But taxing Netflix? Just what does Netflix have to do with urban transit? Next thing you know, someone will propose taxing people for working at home because, you know, homes are “stealing” riders away from transit. Continue reading