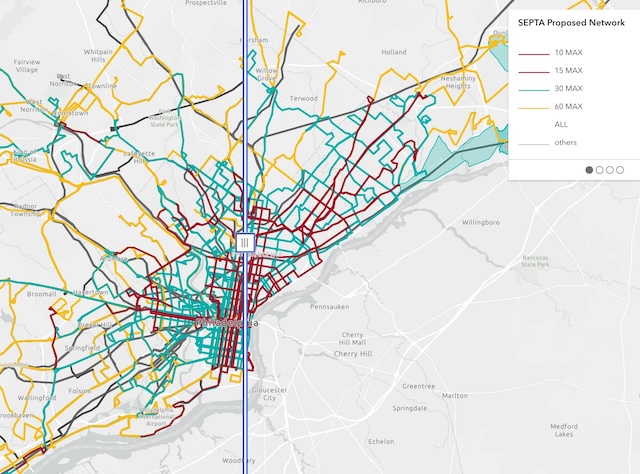
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is planning to revolutionize its bus network next year. While transit systems are due for a revolution, the agency’s plan isn’t revolutionary enough.
Click image to go to a map comparing SEPTA’s current dense bus routes (left) with the proposed sparser bus network (right).
The problem with most bus systems is that they focus on downtowns to the exclusion of the rest of the region. Before the pandemic, half of all workers in downtown Philadelphia took transit to work, but only 8 percent of the region’s workers worked downtown. The bus system did such a poor job of serving the rest of the region that less than 6 percent of workers who didn’t work downtown commuted by transit. Continue reading


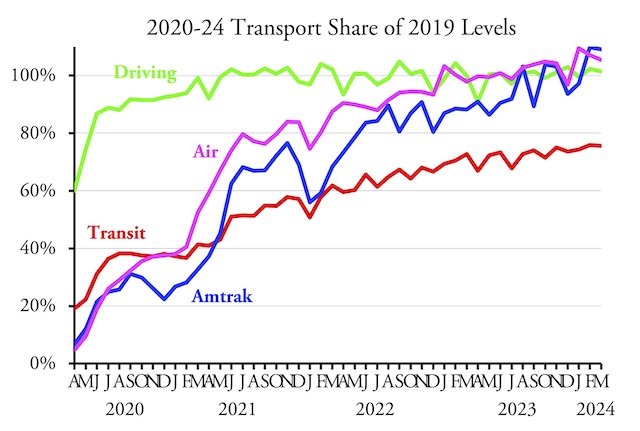

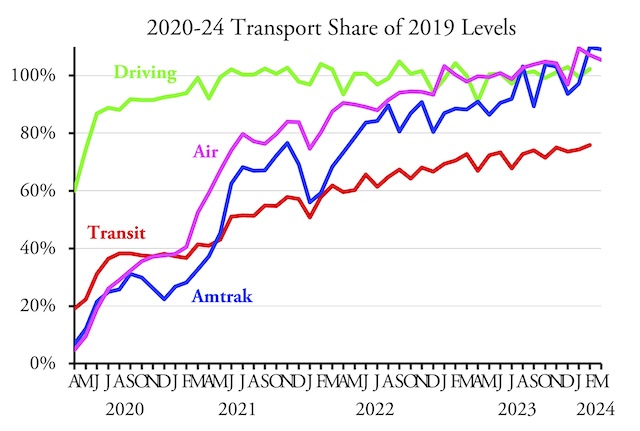


 Americans are 25 times more likely to commute by auto than by transit, but an image search for “commute to work” turns up mostly photos of transit riders.
Americans are 25 times more likely to commute by auto than by transit, but an image search for “commute to work” turns up mostly photos of transit riders. 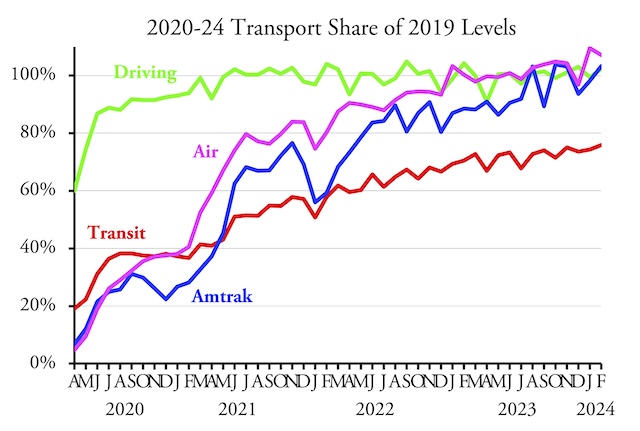 The February 2024 line for driving is obscured by the line for Amtrak, but both are approximately 102 percent.
The February 2024 line for driving is obscured by the line for Amtrak, but both are approximately 102 percent.





