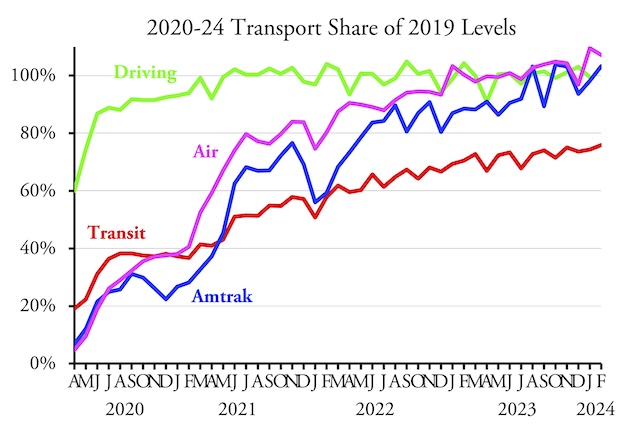
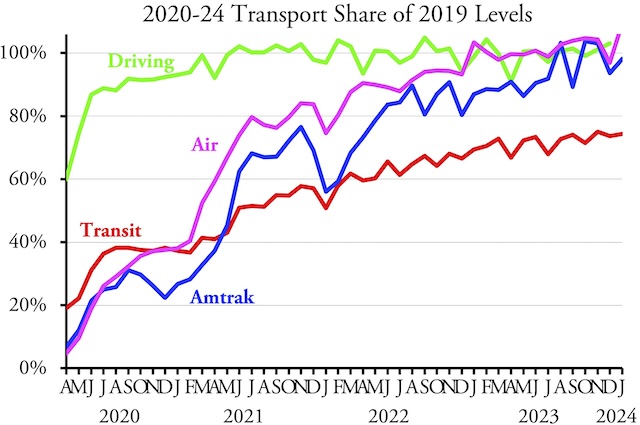
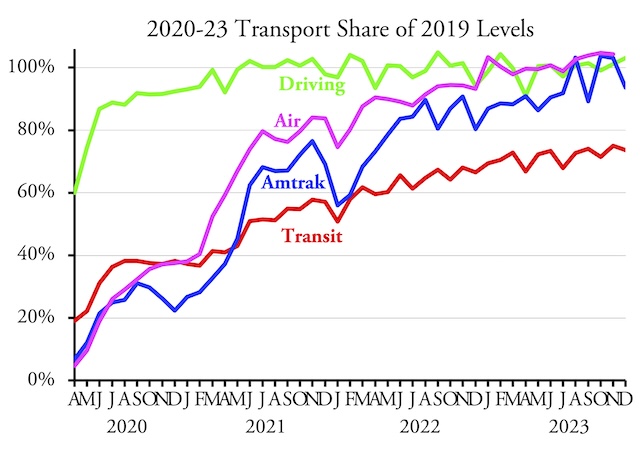
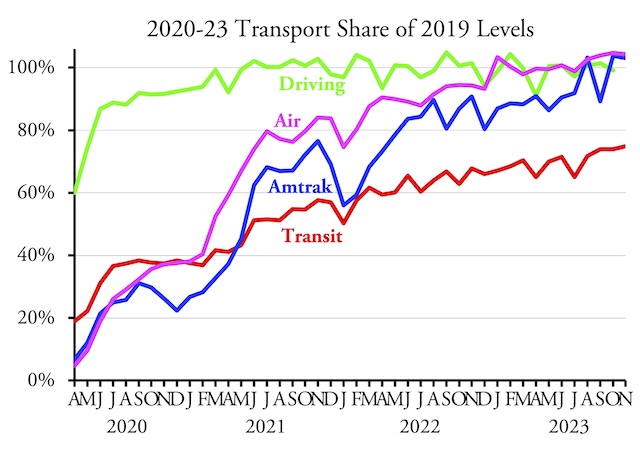
Today is Earth Day, a day in which we are supposed to celebrate environmentally friendly ideas such as public transit, high-density development, and electric vehicles. My report published last week revealed that the transit lobby has hijacked affordable housing funds so that, in many cities, most of those funds are spent on expensive high-density transit-oriented developments rather than on more affordable low-rise housing.
The Federal Transit Administration has recommended that Congress fund the Inglewood Transit Connector, a $2.0 billion people mover that will be just 1.6 miles long.
Last month, the Federal Transit Administration released its 2025 funding recommendations for transit capital improvements. This allows us to see some of the wacky ideas that the transit industry has come up with in recent years. Continue reading