A 3/4-cent sales tax increase for transit is “seen as a game-changing model to fund transit service — and the envy of many cities nationwide,” reports the Minneapolis Star Tribune. What the article doesn’t say is how the tax will change the game for the worse for transit riders and transportation users in general.
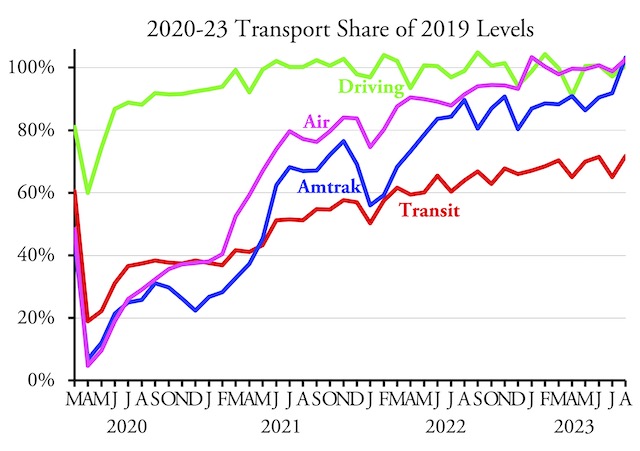
Twin Cities transit ridership had been going downhill before the pandemic, declining nearly 10 percent between 2015 and 2019. Photo by Metro Transit.
What this means is that Metro Transit will no longer care about ridership numbers. Instead, it can freely spend hundreds of millions of dollars a year on projects that do little to generate ridership with no repercussions. Continue reading