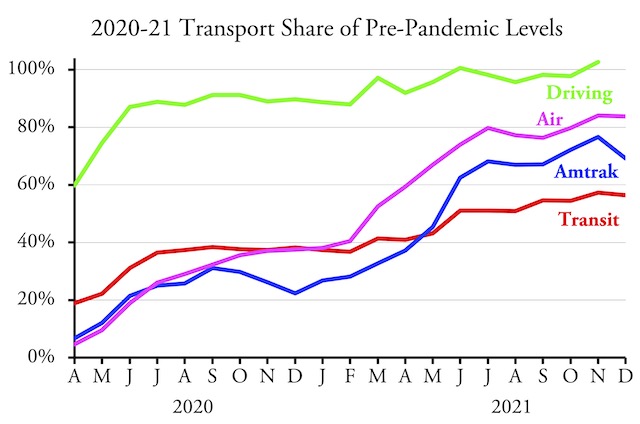
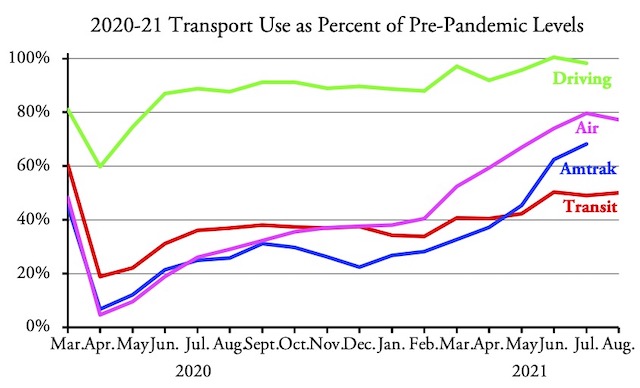
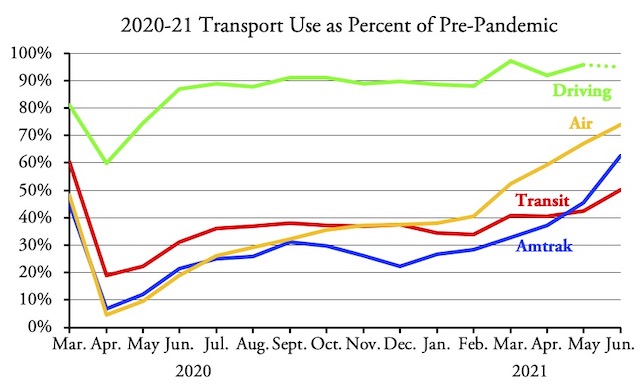
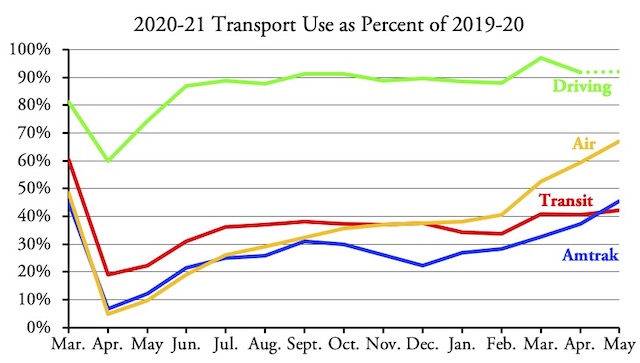
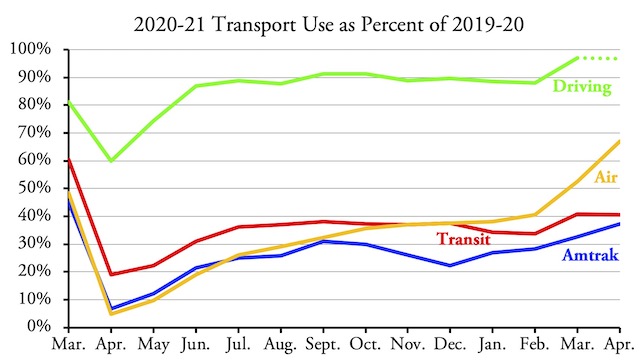
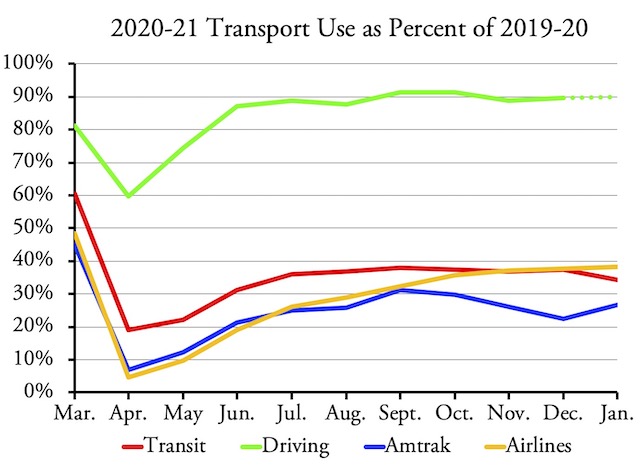
The nation’s transit systems carried 56.2 percent as many riders in November 2021 as in November 2019, according to data released by the Federal Transit Administration on Friday. Though an improvement over October’s 53.5 percent, transit still lags behind the airlines, at 84.0 percent, and Amtrak, at 76.6 percent.
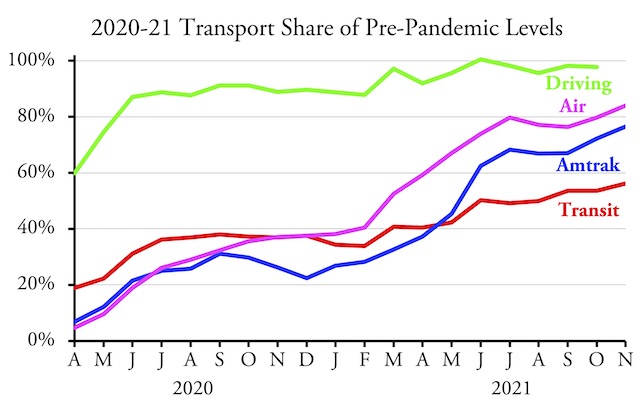
Amtrak numbers from its Monthly Performance Report; airline numbers from the Transportation Security Administration; November highway numbers will be available in a week or so.
Transit bus ridership numbers were up to 60.5 percent of pre-pandemic levels while rail numbers reached 52.2 percent. Ridership has still failed to reach 50 percent of pre-pandemic numbers in Detroit (35.4%), San Francisco-Oakland (45.0%), Washington DC (45.5%), Sacramento (48.4%), San Jose (49.1%), and Chicago (49.8%). At the other extreme, ridership has recovered the most in Los Angeles (72.1%), San Diego (64.7%), Tampa-St. Petersburg (63.9%), Las Vegas (63.4%), Dallas-Ft. Worth (62.6%), Houston (61.2%), and San Antonio (60.6%). The New York urban area, which produces about 45 percent of all transit numbers in the U.S., was slightly above average at 58.3 percent. Continue reading →