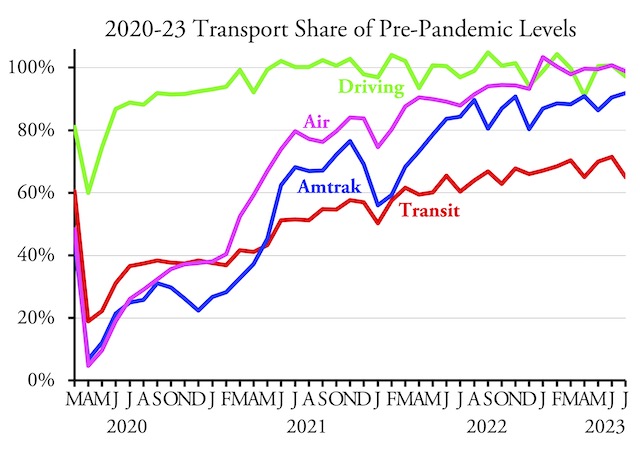
After reaching 70 percent of pre-pandemic numbers in June, transit ridership in July fell back to 65 percent of July 2019, according to data released last week by the Federal Transit Administration. Since July 2019 had 22 working days while July 2023 only had 20, this decline is not surprising.
Meanwhile, Americans drove 97.2 percent as many miles in July 2023 as in the same month of 2019, according to Federal Highway Administration data released last week as well. Amtrak’s monthly performance report indicates that the railroad carried 91.2 percent as many passenger-miles in July 2023 as July 2019, while the Transportation Security Administration says that 98.8 percent as many travelers passed through security in July as in 2019. Continue reading