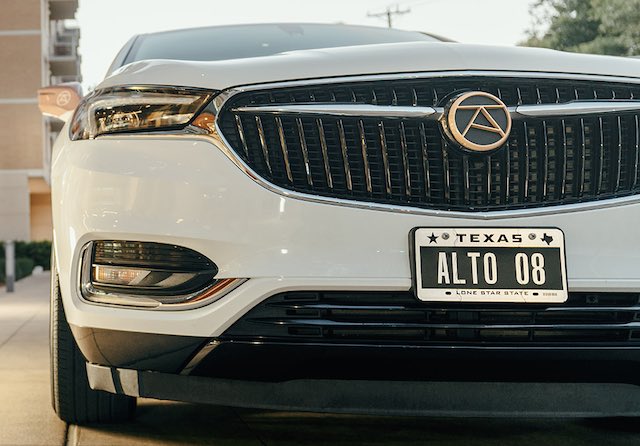
Alto is a rideshare company that was founded in Dallas and so far is also operating in Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, San Francisco, and Washington. The company differs from traditional rideshare operations like Uber and Lyft in that it owns all of its automobiles and all of its drivers are employees, not contractors. This is supposed to make it more attractive to passengers, especially women, who may be squeamish about riding in a stranger’s car.
Photo courtesy of Alto.
Alto claims that its rides are “elevated” above other ridesharers. Its fleet currently seems to consist of Buick Enclaves, a cross-over with three rows of seating. It has replaced the Buick logo on the grill with its own and added its logo to other parts of the vehicles as well. However, it plans to transition soon to all-electric vehicles. Continue reading