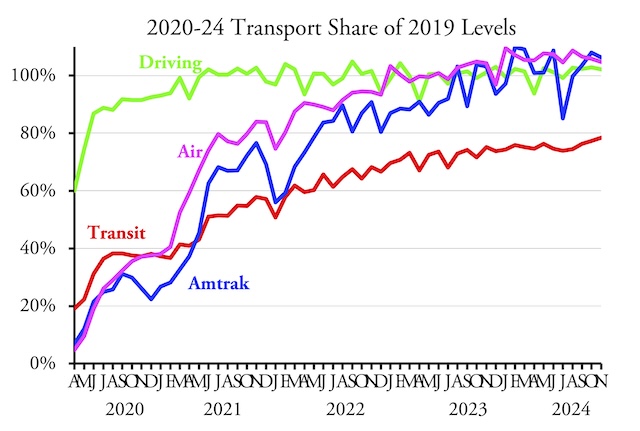
Americans drove 2.2 percent more miles, flew 4.7 percent more trips, and took Amtrak 6.2 percent more passenger-miles in November 2024 than the same month before the pandemic, according to data recently released by federal agencies. Transit ridership, however, still lagged almost 22 percent behind pre-pandemic numbers.
For once, the Federal Highway Administration, Federal Transit Administration, and Amtrak all released their monthly data reports at about the same time, late last week. TSA passenger counts are available only a day or two after each day, but I generally wait for data from other agencies before posting the airline data. Continue reading