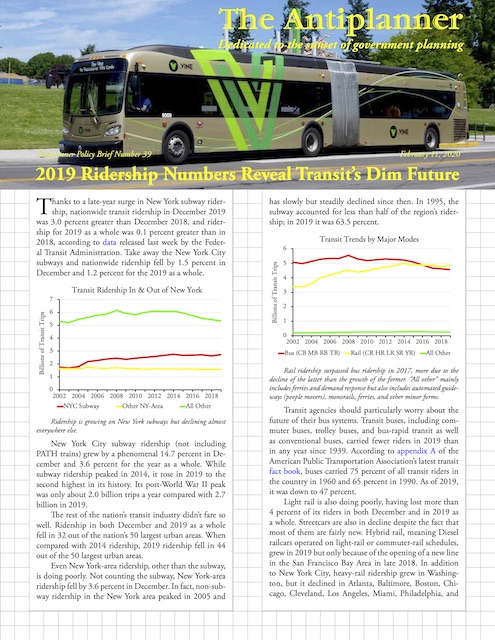
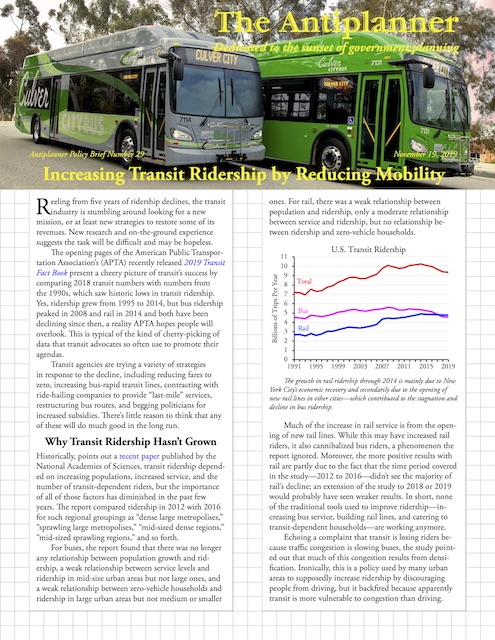
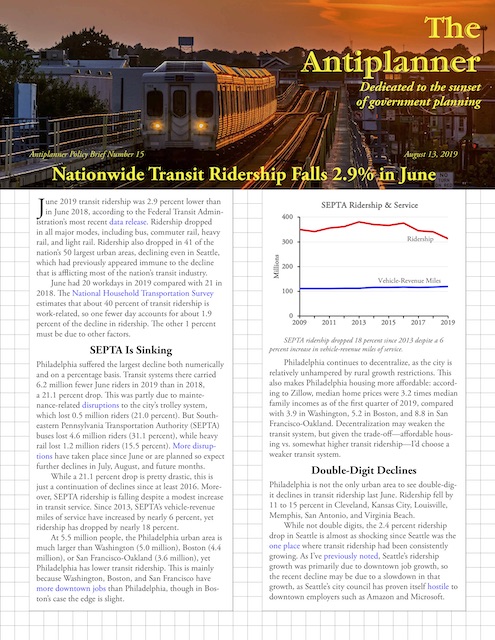
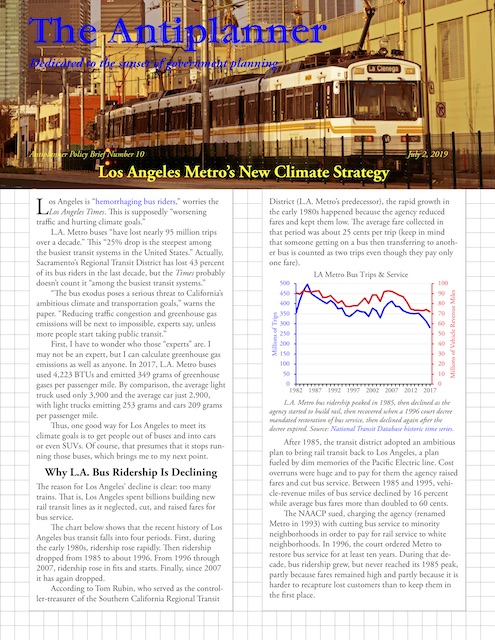
An op-ed in InsideSources argues that public transit should be shut down as it is a major source of viral infections. No one reading this will be surprised that the Antiplanner wrote the op-ed, but the Antiplanner isn’t the only one who thinks so.
Writing in yesterday’s USA Today, University of Tennessee law professor Glen Harlan Reynolds points out that “mass transit kills.” I know some commenters on this blog point out that New York subways didn’t have to be as deadly as they were, but just two months ago people didn’t know enough about the virus to know how to protect themselves, with some experts (relying on misinformation from China) even arguing that masks could do more harm than good. Since each infectious disease is different, the safest course is to avoid public transportation.
New York City shut down its subways yesterday morning for the first time in its history. The goal is to give crews a chance to disinfect subway cars and stations and open them up again, but just overnight may not be enough as cars can quickly become reinfected every morning. Continue reading