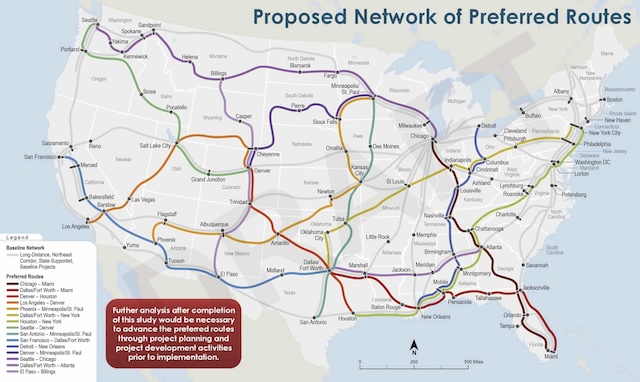
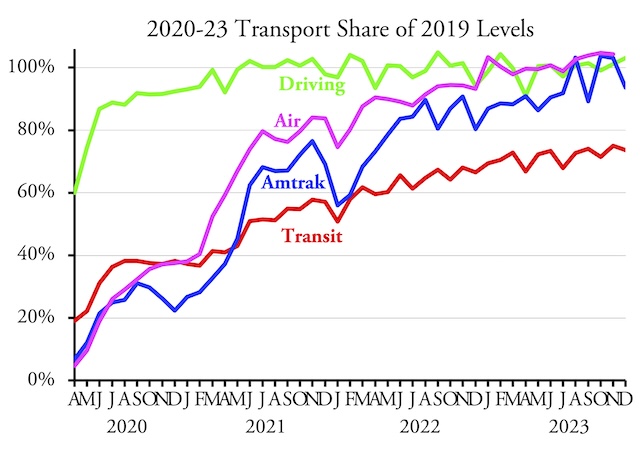
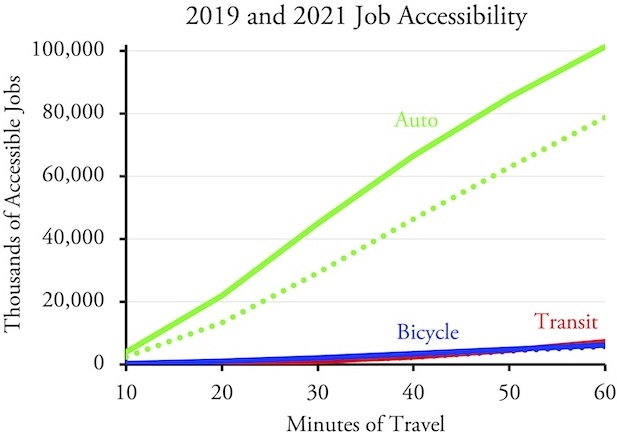
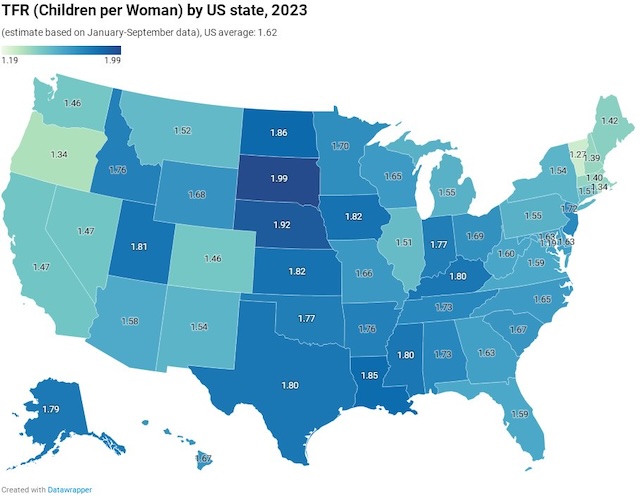
Section 24220 of the 2021 infrastructure law directs the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to require that automakers include a device in new cars that will passively detect whether the driver is drunk and keep them from operating the car. NHTSA has until November of this year to write the rule and then new cars made beginning two years after that must comply. The law specifically states that if NHTSA can’t find a device that will accomplish this, then it doesn’t have to require one.
U.S. Navy photo by Photographer’s Mate 2nd Class Nathanael T. Miller.
This law has led to fears that the government will require automobiles to have “kill switches” that the government can remotely control, thus shutting down people’s freedom of mobility at any time. Defenders of the policy argue that these fears are overblown. Last month, NHTSA issued its advance notice of proposed rule making on the subject and it’s worth looking at it before comments are due next Tuesday, March 5. Continue reading