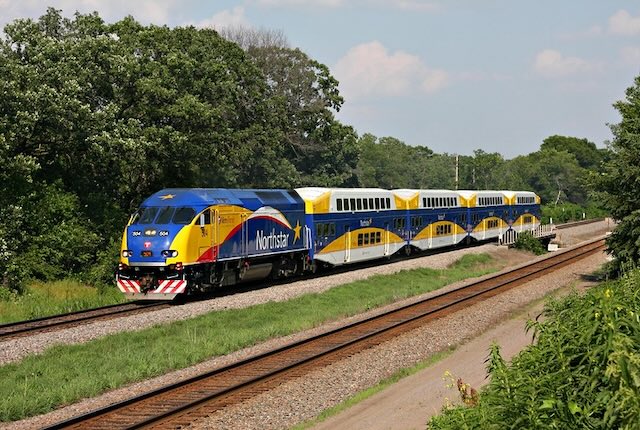
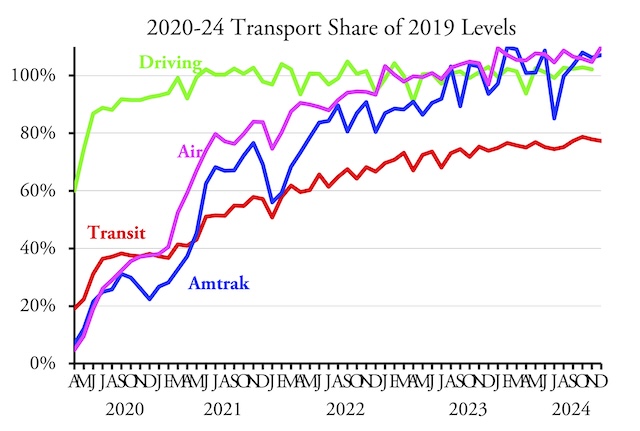
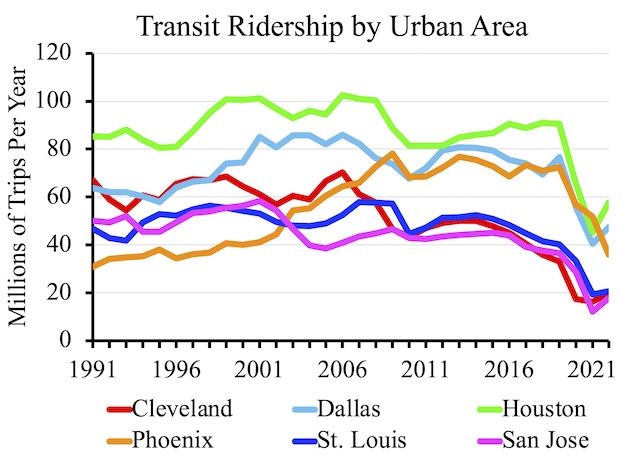
“Billions spent, but fewer people are using public transportation,” declares the Los Angeles Times. The headline might have been more accurate if it read, “Billions spent, so therefore fewer are using public transit,” as the billions were spent on the wrong things.
The L.A. Times article focuses on Los Angeles’ Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro), though the same story could be written for many other cities. In Los Angeles, ridership peaked in 1985, fell to 1995, then grew again, and now is falling again. Unmentioned in the story, 1985 is just before Los Angeles transit shifted emphasis from providing low-cost bus service to building expensive rail lines, while 1995 is just before an NAACP lawsuit led to a court order to restore bus service lost since 1985 for ten years.
The situation is actually worse than the numbers shown in the article, which are “unlinked trips.” If you take a bus, then transfer to another bus or train, you’ve taken two unlinked trips. Before building rail, more people could get to their destinations in one bus trip; after building rail, many bus lines were rerouted to funnel people to the rail lines. According to California transit expert Tom Rubin, survey data indicate that there were an average of 1.66 unlinked trips per trip in 1985, while today the average is closer to 2.20. That means today’s unlinked trip numbers must be reduced by nearly 25 percent to fairly compare them with 1985 numbers.