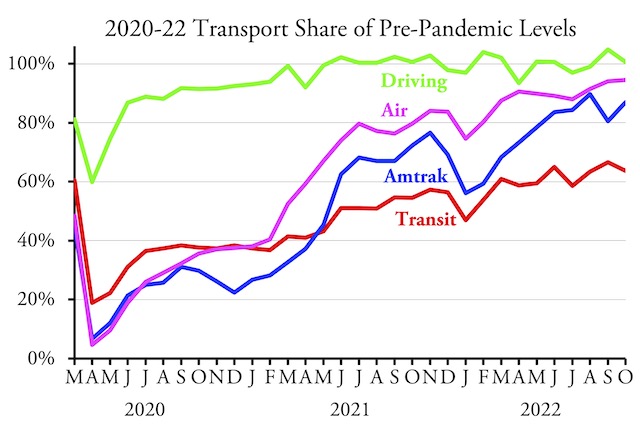
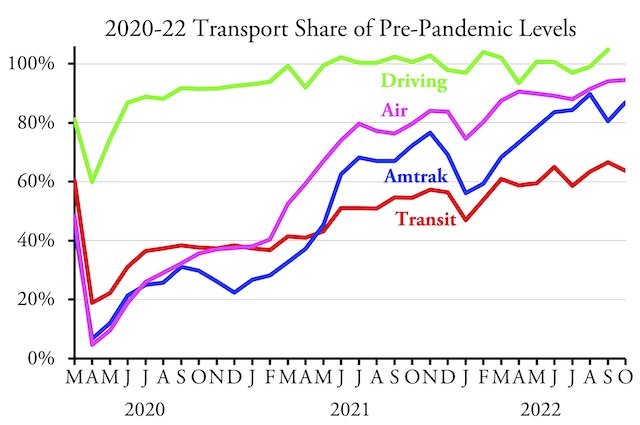
Americans drove 0.6 percent more miles in October 2022 than the same month in 2019, according to data released yesterday by the Federal Highway Administration. This is the second month in a row and the twelfth month in all that driving exceeded pre-pandemic levels since the pandemic began.
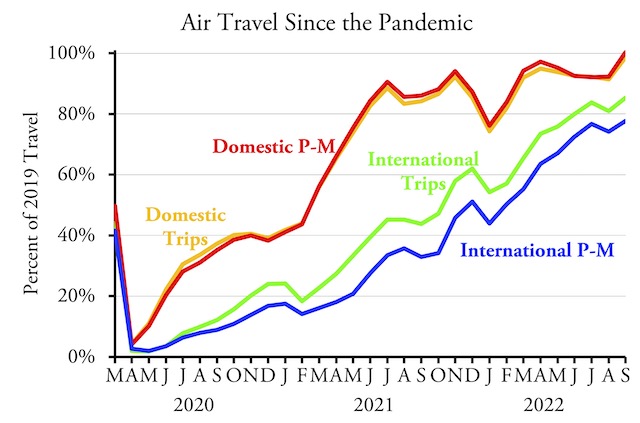
See previous posts for information about data from Amtrak and transit and air travel.
Driving exceeded 2019 miles in 26 states, while it fell short in 24 states and DC. The states that saw the greatest increase in driving, relative to October 2019 miles, were South Dakota (22.6%), Arizona (18.8%), Rhode Island (17.6%), Montana (15.4%), Missouri (11.2%), and South Carolina (11.1%). States that are still furthest from full recovery include California (-8.7%), Massachusetts (-8.0%), Delaware (-8.0%), Pennsylvania (-7.4%), and Maryland (-6.1%). Also, DC is -12.6%. Continue reading