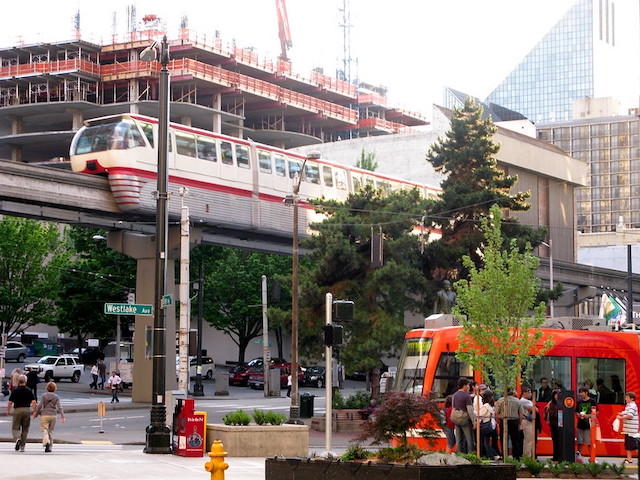
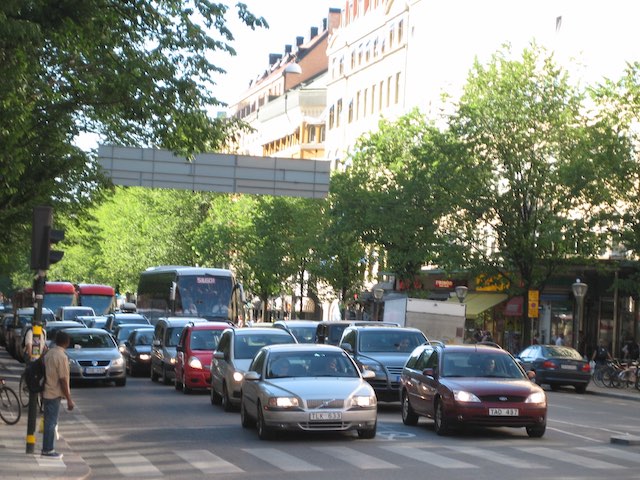
Kimberly Nicholas, an associate professor of sustainability at Sweden’s Lund University, says that automobiles are killers and offers twelve ways to get them out of our cities. Typically for sustainability advocates, she completely ignores the benefits provided by automobiles as well as ways in which the costs of automobiles could be reduced without reducing driving.
A typical street in sustainable Stockholm. Photo by European Institute for Sustainable Transport.
Her twelve ways include reducing the amount of parking, charging more for parking, closing parts of cities to automobiles, and charge a fee to drive automobiles into city centers. All revenues from such fees, parking, fines, etc., should, in her opinion, go to fund “sustainable transport,” which means any kind of transportation other than automobiles. Continue reading


 Not getting much use: a Sound Transit ticket machine.
Not getting much use: a Sound Transit ticket machine.